Optimal acid-alkaline balance in the body (pH): the key to good health

It has long been known that the acid-alkaline balance in the human body is like a golden key to good health and well-being. Today, however, traditional medicine has been forgotten, while in natural medicine and alternative medicine this is one of the basic elements.
Human life (aging) is basically the process of acidosis of the body. Inappropriate food, drinks, tobacco, excessive physical and mental strain, stress – all this creates an acidic environment and has negative consequences. The body works all the time, using energy to neutralize this acidic environment, because only in an alkaline environment is it adequately supplied with oxygen, nutrients and protected from cell and tissue damage.
So, the more successfully we manage to maintain a constantly alkaline environment, the healthier we will be, also the better we will look and feel.
What is the acid-alkaline ratio?
All life processes take place in a liquid median, with a certain concentration of hydrogen (H) atoms. Substances that give away H atoms are called acidic, those that collect H atoms are called alkaline. The specific ratio of acid to alkaline in any solution is called the acid-alkaline balance. This unit is usually are presented on a scale and the abbreviating letters pH (abbreviation of power Hydrogen).
The pH level depends on the ratio of positively (acidic) and negatively (alkaline) charged ions.

The body constantly tries to balance the acid-alkaline ratio, maintaining a strict pH level in internal fluids (blood, lymph, intercellular fluid, saliva, etc.). Body fluids should be weakly alkaline. Blood pH is ~ 7.43, lymph 7.35-7.4, intercellular fluid 7.26 – 7.36. The only acidic fluids in the body are stomach juice and urine. Most enzymes also only function under strictly defined conditions where the pH is between 7.3-7.4. Even small changes reduce the activity of enzymes and the speed of biochemical processes.
For vital processes (homeostasis) to be normal, the pH of the body’s internal environment must be constant. If the blood pH increases by 0.15%, the body becomes alkaline, thus the free oxygen is able to be absorbed 65% better. Conversely, all disease-causing microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi) appear in those parts of the body that are poorly supplied with oxygen.
How does the body regulate pH balance?
In order to neutralize the acidic environment, especially in the blood, the body must have access to its alkaline reserves – minerals (Calcium, Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium, Iron). A significant decrease in alkaline reserves weakens all organs and therefore the systems surrounding those organs, leading to the development of acidosis symptoms. The body should have a slightly alkaline environment, under such conditions, energy formation, protein, lipid synthesis, mineral metabolism, etc. are more active. But in reality, for most people, the body is slightly “acidic”. A constant acidic environment in the body can lead to metabolic disorders and related complications not only in the cells, but in the body as a whole.
The body has a buffer reaction, which means that if the blood is too acidic, this acid is released into the body’s tissues to balance the blood pH level and issues such as gout can develop. If there is not enough acid in the blood, it is collected from the tissues accordingly.
For example, the development of oncological diseases is an anaerobic process. This means that when the body lacks oxygen, the formation of cancer cells is stimulated because the body fluids are “acidified”.
Acidification of the body
Why increased acidity in the body is harmful?
When the body cannot deal with acidity, it stores it in the body tissues, where all the nutrients and information are exchanged between the cells. In connective tissues, acid metabolic residues become an obstacle to the normal functioning of the body’s systems. These acidic residues become like a foreign body, creating a constant risk of inflammation.
Large, acidic deposits of toxins in connective tissue are often visible to the naked eye as cellulitis occurs (acidification of adipose tissue).
If a lot of acids are involved in metabolism, it has a negative effect on blood circulation. Red blood cells, moving through acidic tissues, lose elasticity, clump and form small thickenings, commonly known as clots. If the doctor makes a diagnosis of micro thrombosis, then it is already a strong acidification of the body. Depending on the location of the blood clots, disorders may occur: myocardial infarction, cerebral hemorrhage, temporary cerebrovascular accident, or limb circulatory disorders.
Unlike alkalis, acids are difficult to remove from the body. It needs to be neutralized at the beginning. However, in order for an acid to become neutral in pH, substances that bind these acids are needed, therefore, neutral salts are formed.
What happens in the cells at acidification?
Under normal conditions, an alkaline reaction occurs in the cell’s internal environment, which depends on a sufficient amount of alkaline mineral salts in the body. If the blood supplying the cells becomes slightly acidic, the cells have to “donate” their mineral reserves. As a result, the cellular environment itself becomes acidic.
Symptoms of acidosis (the body is too acidic):
- Constant fatigue, weakness, feeling cold, poor immunity;
- Muscle inflexibility, stiffness, skeletal demineralization, joint “cracking”, bone and joint pain;
- Shoulder and neck muscle tension;
- Arthritis and ligament injuries;
- Sand and /or stones in the kidneys, gallbladder;
- Abdominal pain, nausea, gastritis, gastrointestinal ulcers, increased stomach acid, constipation;
- Bitter taste in the mouth, gray-white plaque, saliva with an acid reaction;
- Deviating gums, inflamed gums, tooth sensitivity, exposed tooth roots and tooth decay, tartar formation;
- Physical and mental fatigue quickly occurs;
- Redness of the face, dark circles under the eyes;
- Osteoporosis, rickets, bone fragility, gout;
- Thin, brittle nails, layered, with white spots and bumps;
- Leg cramps and spasms;
- Frequent ARV (popularly called a cold);
- Skin diseases (psoriasis, eczéma, Atomic dermatites, etc.) ;
- Low hemoglobin level;
- Lack of life force and energy.
If the internal environment is acidic, the body spends a huge amount of energy to restore acid-alkaline levels. There is also fatigue, and later various ailments and diagnoses.
The main causes of acidification:
- Consumption of acidic products and drinks. Not literally, but causing an acid reaction in the body;
- Too much meat and /or fish in the diet;
- Too much refined carbohydrate (especially sugar and white flour) in the diet;
- Lack of fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet;
- Alcohol consumption;
- Tobacco;
- Hard physical work, mental load;
- Stress;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Dirty air (heavy metals);
- Excessive exercise – too much load.
Consequences of acidification of the body:
- Consistant acidic environment in the body leads to burnout. In order to reduce the concentration of acids and remove them from organs and tissues, the body retains water, thus slowing down metabolic processes. In this way, the body “wears out” faster, ages, the skin becomes dry, with wrinkles, various diseases appear;
- Too acidic reaction in the urine – a great environment for the formation of sand and stones in the kidneys. Chronic renal impairment causes inflammation of the urinary system, reproductive system, and renal failure. This in turn leads to a weakening of organs and systems;
- The acidic reaction of saliva degrades tooth material and can cause stomatitis (inflammation of the lining of the mouth);
- Chronic acidification of the body can cause headaches, anxiety, insomnia.
Alkaline minerals
As mentioned above, if the body’s environment is too acidic, it must be neutralized, the pH balance must be restored, which is done with the help of alkaline minerals, they are removed from various tissues of organ systems.
Magnesium (Mg)
The amount of Mg in the body is ~ 21-28g. About 60% of it is found in bones, teeth, 20% in muscles, 19% in other energy reserve organs: brain, heart, liver, kidneys. 1% is in the intercellular fluid. Without this mineral, calcium absorption is not possible.
Biological properties of magnesium:
- One of the main energetics of cells. All energy processes in the body take place in the presence of magnesium;
- Protects the nervous system from stress and psycho-emotional stress. There is an insulating material for the nerve impulse, it regulates;
- Maintains urine salts in a liquid dissolved state, even in small concentrations destroys crystallization and stone formation in the kidneys;
- Participates in reducing the harmful effects of toxins in the liver, protects against radiation and heavy metals;
- Necessary for strengthening bone tissue, strengthening teeth, hair, nails;
- Regulates memory, mood, heart rate, vascular tone, gastrointestinal tone.
Effects of magnesium deficiency on connective tissues
Magnesium plays an important role in the formation of the normal structure of connective tissues (bones, ligaments, cartilage, hair, nails, teeth, skin, adipose tissue, etc.). If there is a deficiency of magnesium, the level of collagen degradation increases, collagen with defects is synthesized due to a disturbed collagen structure, the ratio of collagen and elastic fibers is degraded, the synthesis of molecules of all connective tissue structures is slowed down.
Causes of magnesium deficiency:
- Too frequent consumption of sweets and caffeine. Magnesium is excreted by the urine;
- Use of refined products;
- Fast-food;
- Frequent use of alcohol;
- Gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes;
- Frequent use of preparations that promote bowel movements;
- Medicines;
- Excessive physical or mental strain, stress.
Magnesium in the diet: spinach, beetroots, pumpkin seeds, soybeans, black beans, sunflower seeds, brown rice, oats, tofu, almonds, papaya, green peas, tuna, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, blueberries, tomatoes, melon, millet.
Calcium (Ca)
50% of people over the age of 40 are calcium deficient. Upon reaching the age of 60 this number increases to 90% deficient.
Calcium deficiency is the cause of ~ 147 diseases, including osteoporosis, arthritis, hypertension, seizures, pregnancy complications, insomnia, oncology, etc.
Calcium regulates internal processes such as intercellular signaling, blood clotting, nerve and muscle function, enzymes and hormones.
Calcium in the body:
- Is the main structural element in the bones;
- Affects the permeability of cell membranes;
- Participates in the transmission of nerve impulses;
- Provides muscle contraction, tension;
- Participates in blood clotting at all stages;
- Participates in the regulation of enzyme activity.
Calcium is most found in the following food products: sesame seeds, cheese, cottage cheese, cabbage, various beans, eggs, sardines, rye bread, shrimps, chocolate, almonds, dates, raisins, oranges, spinach, corn.
Sodium (Na)
The daily dose of sodium for adults is ~ 4-6g. Sodium metabolism is regulated by the kidneys whose function help maintain blood and other body fluids.
Sodium in the body regulates the osmotic pressure of intercellular fluid and together with potassium provides permeability of cell membranes, allowing water to circulate.
Sodium ions are needed to transmit nerve impulses, it activates several enzymes.
Sodium containing products: sea cabbage, mussels, lobster, octopus, flounder, anchovies, shrimp, sardines, egg, crab, squid, greens.
Iron (Fe)
Iron in the body:
- Improves the condition of skin, hair, nails;
- Indispensable in hematopoietic and cellular metabolic processes;
- Containing hemoglobin. Responsible for oxygen transport;
- Is a component of enzymes and cytochromes;
- Normalizes thyroid function;
- Affects the metabolism of B vitamins;
- Necessary for the growth of the organism;
- Regulates immunity (activates interferon activity and cell-killer activity);
- Acts as a toxin neutralizer.
Iron in food products: egg yolk, beef, sea cabbage, chicken, beans, pork liver, mussels, pumpkin seeds, spinach, buckwheat, dried apricots, apples.
Potassium (K)
Potassium provides cell permeability and is responsible for the mechanism by which energy enters the cell. Potassium regulates the cardiovascular system and is very difficult to ingest with food.
How to help the body maintain pH balance?
There are hundreds of ways the body can be acidified, but there are only 4 ways to alkalize it:
- To perform sauna and sauna rituals more often, because with increased sweating the acidic metabolic end products are released from the body;
- Eat more alkaline foods;
- Drink alkaline water;
- Regular cleansing of the body, including deep cleansing.
More detail about alkaline food and alkaline water.

The daily diet of a healthy person should be at least 50% alkaline food, in some scientific publications figures as heigh as 75-85% are quoted. If a person becomes ill, alkaline products should make up 90% of the diet.
The acidic and alkaline division of food is determined by its final reaction in the blood.
An extensive list of acidic and alkaline products can be found on various websites and in literature. The following is a brief list:
Acidic products: meat, fish (lean), sweets, pasteurized dairy products, flour products, canned food, alcohol, coffee, black tea, chocolate, tobacco, etc.
Neutral products: buckwheat, paddy rice, meal, crude vegetable oils, oats, barley, etc.
Alkaline products: almost all fresh vegetables (zucchini, broccoli, spinach, all types of cabbage, maize, carrots, butter beans, peppers, beets, avocados, garlic, onions, pumpkin, cucumber, radish, etc., except tomatoes and auberges) and fruit (melons, grapes, apricots, apples, pears, even sour-citrus, pineapple), various sprouts, all greens, unpasteurized honey, herbal infusions, soaked almonds, soaked walnuts, sea cabbage, eggs, fatty fish (e.g. salmon), everything that is bitter, etc. Legumes are also included in alkaline products, but they must be thoroughly soaked before eating, which aids the digestion and absorption of these products, as well as deactivates substances that adversely affect enzyme activity.
Alkaline water
The easiest way to reduce the acidic environment of the body and alkalize it is to drink enough alkaline water every day – at least 1.5 l, or preferably 30 ml per 1 kg of weight. When cleaning or if we want to get rid of excess weight – even 40ml per 1 kg of weight. The water must also be bioavailable; it must be easily absorbed in to the body. To achieve bioavailable water the surface tension between the water molecules should not be too high, simply put, the water should be fluid enough to be absorbed into the cells. Also, the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) of water should range from -100 to -200 mV (millivolts), which is the same as that of intercellular fluid, the body will therefore not need to consume extra energy to balance this ORP.
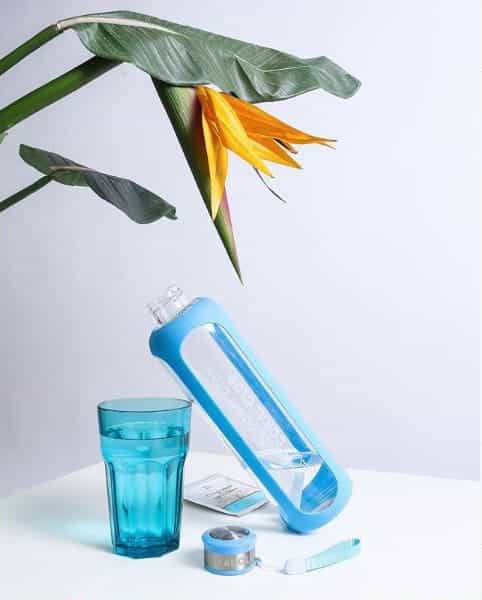

The powerful antioxidant H-500 is also very effective in making water alkaline. It contains alkaline minerals – magnesium, potassium, silicon and sodium. If one capsule H-500 is added to the water, its ORP reaches -500mV!
H-500 features:
- Neutralizes free radicals;
- Restores the alkaline environment in the body;
- Provides the body with energy;
- Multiplies the absorption rate of nutrients into cells;
- Reduces blood lactic acid levels by 50% (athletes);
- Increases mental abilities;
- Improves response, brain microcirculation;
- Restores working capacity, etc.
Registration in Coral Club
Please fill out the registration form and you will receive a unique Club Member ID (CCI ID), you will become a Club Member and you will be able to purchase products with a 20% discount and will have access to other benefits.
Registration of discount card
Please carefully read the terms of registration using the referral link:
- Clicking this link, you confirm your desire to join Coral Club in Liga Rymer’s structure, who becomes your consultant/sponsor;
- By clicking on this link, you confirm your desire to receive information about the company’s products, the concept of health of its application and the principles of the company’s work in English.
I agree
Registration form
You can contact us, if you have any questions.
Dietary supplements do not replace a full and balanced diet and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
The information on this website is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendation.
The products and Health Concept serve as support for the body's natural processes at the physical level, but improving health requires a comprehensive approach – lifestyle changes, dietary habit improvements, physical activity, stress management, and mindset shifts.
Before using any dietary supplements or making changes always consult your doctor or a certified healthcare specialist.